Creating a PowerBuilder .NET Web Forms target
System requirements
You must install the .NET Framework
2.0, 3.0, or 3.5 SDK (x86) and AJAX Extensions on the same computer
as PowerBuilder, and you must make sure that the system PATH environment
variable includes the location of the .NET Framework. If you installed
a 1.x version of the .NET Framework, you must make sure the PATH
variable lists a supported version first.
You must also install the .NET Framework and AJAX Extensions
on the IIS server where you deploy a .NET Web Forms target.
For more information about installation and configuration,
see “Configuring ASP.NET for
a .NET project”.
For information on migrating .NET Web Forms targets from earlier
releases of PowerBuilder, see the section on “Migration
information” in the current Release Bulletin
.
If you are deploying .NET applications from a computer with
the Vista operating system, you must run PowerBuilder as the computer
administrator.
About the .NET Web Forms target
You can use the PowerBuilder .NET Web Forms Application target
wizard to create a Web Forms target “from scratch” or
from an existing PowerBuilder application.
The existing application object that you select to use as
a Web Forms application can be an application object from any type
of PowerBuilder target. By default, if the existing application
is already included in a target in the current workspace, the wizard
reuses the entire library list from the existing target as the library
list for the Web Forms target that the wizard creates.
After the wizard creates a Web Forms target from an existing
application, all objects from that application are visible in the
System Tree for the Web Forms target except project objects for
other types of PowerBuilder targets.
About the .NET Web Forms project
Whether you use the target wizard to create a new target from
scratch or from an existing application, the target wizard always
creates a new project. It automatically launches the .NET Web Forms
Application project wizard. A .NET Web Forms project object is required
to deploy the Web Forms application to an IIS 5.0 or later server.
Once the application is deployed to a server, end users can run
it from a Web browser.
Although you can always start the .NET Web Forms Application
project wizard from the Project tab of the New dialog box, you can
start it for a .NET Web Forms target type only. If the current workspace
does not have a target of this type, PowerBuilder does not let you
run the .NET Web Forms Application project wizard.
Table 2-1 lists
optional and required items in the .NET Web Forms Application project
wizard:
| Wizard field | Description |
|---|---|
| Project name | Name of the .NET Web Forms project. |
| Project library | Library where you want to store the .NET Web Forms project. |
| Web application name | Name of the .NET Web Forms application. By default, this is the name of the application for the current PowerBuilder target. |
| Application URL preview | Address for starting the .NET Web Forms application in a browser (minus the default.aspx or default.htm start-up file name). |
| Resource file and directory list | Specifies a list of resource files, or directories containing resource files, that you want to deploy with the project. When you select a directory, the resource files in all of |
| Win32 dynamic library file list | Specifies any Win32 DLLs that you want to include with your project. Modules in this list are deployed to the bin directory in the application Web site under the virtual root folder. |
| JavaScript file list | Specifies JavaScript files you want to deploy with the project. |
| Generate setup file option and Setup file name |
Select this option and a setup file name if you are not deploying directly to an IIS server. |
| Direct deploy to IIS and IIS server address | Select this option to deploy to an IIS server and enter the address of the server where you want to deploy the .NET Web Forms application. |
Using the .NET Web Forms Project painter
After you click Finish in the project wizard, PowerBuilder
creates a .NET Web Forms project and opens the project in the Project
painter. The Project painter displays the values you entered in
the wizard and allows you to modify them. The painter also includes
functionality that is not available in the .NET Web Forms Application
project wizard.
| Project tab page | Functionality not available in the .NET Web Forms wizard |
|---|---|
| General | Includes the following radio button build options:
You For information on the rebuild scope, see “Incremental rebuild for The General tab also includes the Enable DEBUG Symbol check box |
| Resource Files | The wizard automatically includes the resource files from all subdirectories of a directory that you add to the wizard’s Resource Files page. In the Project painter, a check box displays under the Recursive column for each directory in the Resource Files page list box. You can clear the check box to deploy only the files in the directory that is listed. You can also select a registry XML file that you want to deploy to the File/Common directory for your application. For more information on using registry files, see “Using the registry functions”. |
| Library Files | The Library Files tab has separate list boxes for target libraries (PBLs and PBDs) and for dynamic Win32 library files (DLLs) that you want to deploy with your project. The PBLs you select are generated as PBDs if they contain DataWindow or Query objects. By default, all target libraries are selected, but you need These types of objects must be contained in a PBL file rather |
| Configuration | On this Project painter page, you can modify global properties for the project before it is deployed. You or the application server manager can also change global properties after the project is deployed. For more information about global properties, see “Global Web configuration |
| Version | You can specify version information for the project on this Project painter page. The version information includes values for the product name, company name, description, and copyright, as well as major, minor, build, and revision version numbers for the product, file, and assembly that you generate when you build the project. The values you enter display in the generated assembly file’s Properties dialog box in Windows Explorer. They are viewable on the Web Forms server, but are not typically available to end users of Web Forms applications. |
| Post-build | You can use this Project painter page to select an application, such as a code obfuscator program, to process the generated Web Forms application immediately after it is deployed. You can select different applications for post-build processing of debug and run versions of your project. |
| Security | Lets you configure CAS security zones for your applications, minimizing the amount of trust required before application code is run by an end user. For more information, see “Security settings” and Appendix A, “Custom |
| Run | Contains the Application field where you can enter the path to a browser you want to have run the Web Forms application and the Arguments field where you can enter the URL for the Web Forms application. By default, the path to the Internet Explorer browser is displayed for the Application field. The Arguments field is populated by default with the value for the project’s Application URL Preview, with Localhost as the default server name. |
| Sign | The Assembly group box on the Sign tab page allows you to attach strong name key files to the assemblies that your project generates. |
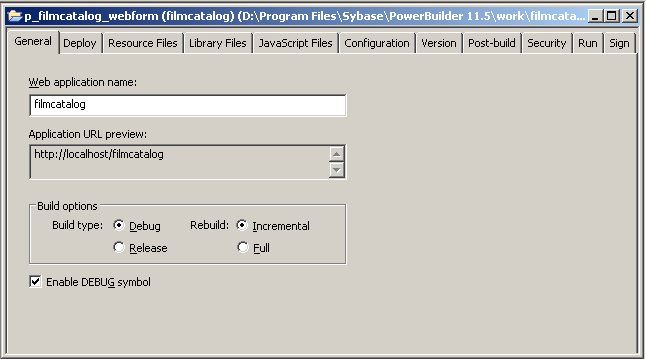
Figure 2-1 displays
the General page of the Project painter for a .NET Web Forms project.
Project painter